Fully hand-held tutorial on setting up the Java environment to a usable state as quickly as possible. Only knowledge of using the terminal is expected. This tutorial will be completely self-contained (excluding links to downloads).
For more detailed tutorials, see General Development Environment Setup Guide
Ubuntu
Java
Open a terminal and run
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jdk openjdk-17-doc openjdk-17-source
Verify installation by opening a terminal and typing
java -version
Gradle
We are currently on Gradle 7. We will install it manually for ease of understanding. The official guide is here for reference. (Aside: we do not use the Gradle Wrapper)
- Download the latest Gradle 7 distribution (7.4.2 as of writing).
- Choose the "complete" version.
- Remember where you downloaded it.
Unpack Gradle (the following are excerpted from the gradle website)
Open a terminal
cd into the directory where you downloaded Gradle. Then
- Unzip the distribution zip file in the directory of your choosing, e.g.:
$ sudo mkdir /opt/gradle $ sudo unzip -d /opt/gradle gradle-7.4.2-all.zip
Add to path
$ echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/opt/gradle/gradle-7.4.2/bin' >> ~/.bashrc
Verify installation
- Open a console (or a Windows command prompt) and run
gradle -vto run gradle and display the version, e.g.:
$ gradle -v ------------------------------------------------------------ Gradle 7.4.2 ------------------------------------------------------------
- Open a console (or a Windows command prompt) and run
- Configure for IHMC software
- Create a gradle.properties file in your user Home directory, ~/.gradle/gradle.properties
Copy/paste below into the file
org.gradle.java.home=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64 org.gradle.jvmargs=-Xmx4g
IDE
This guide currently only contains instructions for IntelliJ. We are working on Eclipse.
Eclipse
Full guide: Eclipse IDE
Intellij
Full guide: IntelliJ IDEA
- Download IntelliJ Community.
- https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/#section=linux
- Open a terminal and cd into the folder where you downloaded the tar file
Extract the file and move it to /opt/. (If you already downloaded from the link above, there is no need to run curl). Replace the names appropriately based on the version you download.
$ curl -sL https://download.jetbrains.com/idea/ideaIC-2022.1.3.tar.gz -o idea.tar.gz $ tar -xzf idea.tar.gz # mv idea-IC-221.5921.22/ /opt/. # rm /opt/idea # ln -s /opt/idea-IC-221.5921.22/ /opt/idea # ln -s /opt/idea/bin/idea.sh /usr/local/bin/idea
IntelliJ is now runnable from the command line:
$ idea
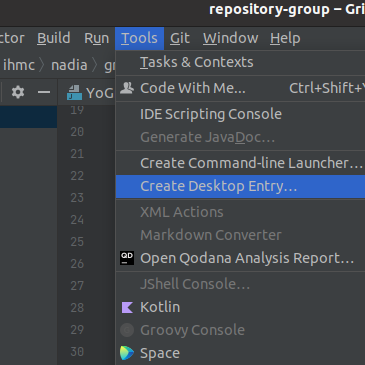
If the desktop launcher is not automatically created, you can open IntelliJ once and select Tools > Create Desktop Entry
- Now you will need to configure IntelliJ to the Java environment you installed.
- Set the Java SDK that you downloaded.
- Go to File > Project Structure > Project Settings > Project.
- Set the <SDK> to Java 17
- Set the <Language Level> to SDK Default.
- Set the gradle version.
- Go to File > Settings > Build, Exectution, Deployment > Build Tools > Gradle.
- Set <Use Gradle From> and select Specified Location. Select the location where you installed gradle to.
- On windows, this will be C:/Gradle/gradle-8.x
- On Ubuntu, this will be /opt/gradle/gradle-8.x
- Set <Gradle JVM> to Project SDK. This should point to the Java SDK you set in the previous step.
- Set the Java SDK that you downloaded.
- Your environment should be ready at this point. Import repository-group.
- File > Open... > select repository-group
- Gradle will take some time to build and index...
- Your projects bar should then look like this (depending on the repositories you cloned):
where all repositories have a blue square on the folder icon indicating they were recognized by gradle as modules.
Windows
Git
- Install Git. Use the 64-bit standalone installer
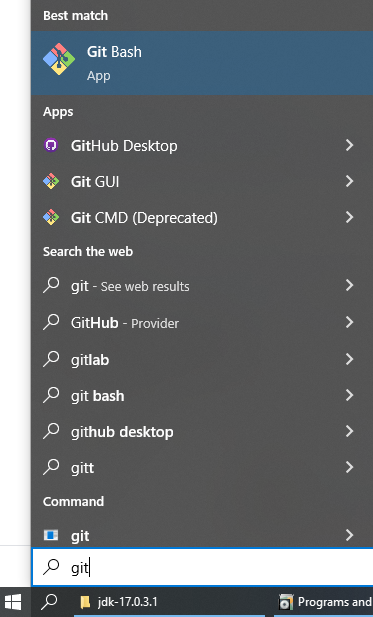
This will be used for all terminal interactions on Windows. Access by searching for Git Bash on the windows search.
Hereby, "open a terminal/console" will refer to launching git bash.
Java
We use Java 17.
- Go to the Oracle download page and download the MSI installer:
This will download Java to the folder (or as appropriate for the version)
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-17.0.3.1
- (Aside: The java path variable is already set using oracle. No action is needed)
- Double-check that java is installed properly:
Open a terminal and type in:
java -version
Something like the following should be outputted:
java version "17.0.3.1" 2022-04-22 LTS Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 17.0.3.1+2-LTS-6) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0.3.1+2-LTS-6, mixed mode, sharing)
Gradle
We are currently on Gradle 7. We will install it manually for ease of understanding. The official guide is here for reference. (Aside: we do not use the Gradle Wrapper)
- Download the latest Gradle 7 distribution (7.4.2 as of writing).
- Choose the complete version.
- Remember where you downloaded it.
Unpack Gradle (the following are excerpted from the gradle website)
- Create a new directory
C:\Gradlewith File Explorer. - Open a second File Explorer window and go to the directory where the Gradle distribution was downloaded. Double-click the ZIP archive to expose the content. Drag the content folder
gradle-7.4.2to your newly createdC:\Gradlefolder.
- Create a new directory
Add to path
- In File Explorer right-click on the
This PC(orComputer) icon, then clickProperties->Advanced System Settings->Environmental Variables. - Under
System VariablesselectPath, then clickEdit. Add an entry forC:\Gradle\gradle-7.4.2\bin. Click OK to save.
- In File Explorer right-click on the
Verify installation
Open a console (or a Windows command prompt) and run
gradle -vto run gradle and display the version, e.g.:$ gradle -v ------------------------------------------------------------ Gradle 7.4.2 ------------------------------------------------------------
- Configure for IHMC software
- Navigate to your user home directory.
- Show hidden files.
- Ensure the existence of the file
~/.gradle/gradle.propertieson Ubuntu orC:/Users/<user>/.gradle/gradle.propertieson Windows. - If it is not there, create it manually. This file's settings will override project and system level settings.
- Copy paste the following lines into the file
Open Source Only:
gradle.propertiesorg.gradle.jvmargs=-Xmx4g
Import Repositories
Don't forget the long paths thing
IDE
Choose your favorite IDE. I like intellij because it was the first IDE I arbitrarily chose to use.
Eclipse
full guide: Eclipse IDE
Intellij
full guide: IntelliJ IDEA
- Download IntelliJ Community. Choose the .exe for convenience
- https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/#section=windows
- All default installation options are fine.
- Now you will need to configure IntelliJ to the Java environment you installed.
- Set the Java SDK that you downloaded.
- Go to File > Project Structure > Project Settings > Project.
- Set the <SDK> to Java 17
- Set the <Language Level> to SDK Default.
- Set the gradle version.
- Go to File > Settings > Build, Exectution, Deployment > Build Tools > Gradle.
- Set <Use Gradle From> and select Specified Location. Select the location where you installed gradle to.
- On windows, this will be C:/Gradle/gradle-8.x
- On Ubuntu, this will be /opt/gradle/gradle-8.x
- Set <Gradle JVM> to Project SDK. This should point to the Java SDK you set in the previous step.
- Set the Java SDK that you downloaded.
- Your environment should be ready at this point. Import repository-group.
- File > Open... > select repository-group
- Gradle will take some time to build and index...
- Your projects bar should then look like this (depending on the repositories you cloned):
where all repositories have a blue square on the folder icon indicating they were recognized by gradle as modules.